At work, friends of the owners often take (or send in) a topographic map and ask whether the plot is suitable for the layout of photovoltaic power plants and the scale of information layout. To answer this question, we first need to identify the topographic map. Xiao Bian will explain the basic knowledge of the topographic map and let everyone understand the topographic map and apply it to the work.
First, the basic elements of the topographic map:
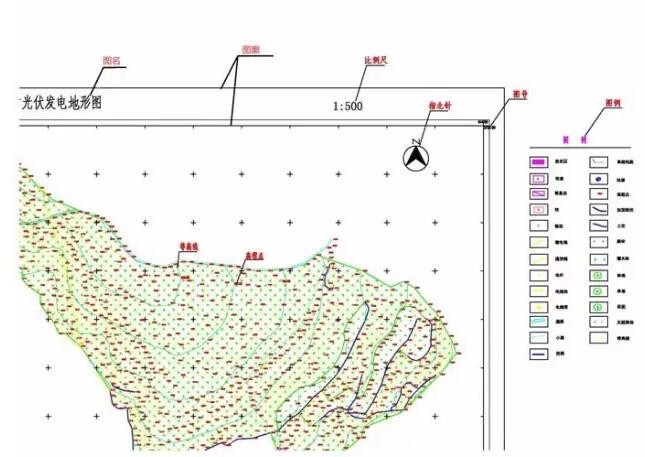
1. Picture name: Each topographic map should be marked with a picture name. Generally, names of places, factories and mines, villages, and project names are used as names.
2, figure number: In order to distinguish the location of the various topographic maps, each topographic map has a figure number. The drawing number is the number of the corresponding division method of the drawing.
3, map: map is the topographic map of the boundary line, there are internal and external maps of the points.
4. Zhibei: In the face of the map, the upper part of the drawing is north, the lower part is south, the left part is west, and the right part is east.
5. Scale: It is a proportional correlation showing the actual distance between the surface and the distance displayed on the map. Scale topographic maps can be divided into three categories: large-scale topographic maps, medium-scale topographic maps, and small-scale topographic maps. The large-scale topographic map refers to 1:500, 1:1000, 1:2000, 1:5000; the medium-scale topographic map refers to 1:10,000, 1:2.5 million, 1:50,000, 1:100,000; small-scale topographic maps It refers to 1:250,000, 1:500,000, and 1:100 million. In the early stages of the project, the scale of topographic maps that we often use is 1:10,000; 1:5000. In the project implementation stage, we often use 1:500; 1:1000; 1:2000.
6. Contour lines: Closed curves connected by adjacent points on the topographic map with equal elevation.
7. Elevation point: The number marked on the contour line, that is, the altitude above this height line.
8. Legend: It is to explain the meaning of various symbols on the map. There are generally roads, houses, overhead lines, rivers, and lakes.
Second, the main features of topographic maps:
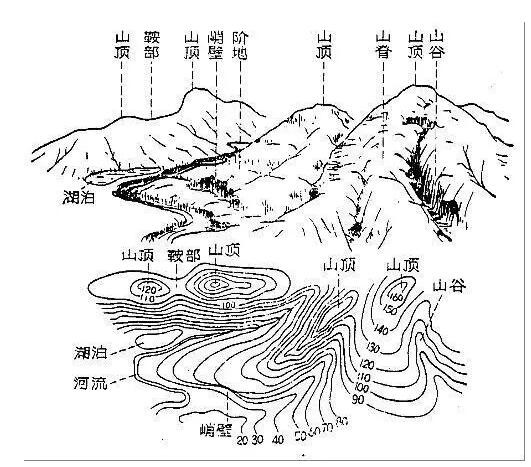
1. Peak: The contour is closed, and the value gradually decreases from the center to the surroundings.
2. Basins or depressions: Contours are closed, and values ​​increase gradually from the center to the surroundings.
3. Ridges: Convex portions of the contour point to lower elevations. The contour line from high to low is the ridge.
4. Valley: Convex portions of the contour point to higher elevations. The contour line from low to high is the valley.
5. Saddle: The gap between the two ridges or valley contour lines that are facing each other.
6. Gentle slopes and steep slopes: The denser the contours, the steeper the terrain; the more sparse the contours, the more gentle the slope.
7, steep cliffs: contours coincide at the cliff.
8. Sunny slope and shady slope: In the topographic map of the contour line, the sunny slope is more sunny, and vice versa.
Third, how to use the topographic map information to determine the feasibility of the site
After understanding the basic concepts of the above topographic maps, I believe we can basically understand the conventional topographic maps. After mastering the information on the topographic map, the terrain map can be used to make initial judgments on the site.
First, determine the north-south east-west direction on the map, and then find the top of the topographic map, so as to distinguish the east slope, west slope, south slope, north slope, and flat land, judge the steep slope, and estimate the area of ​​various slopes.
According to the experience of mountainous photovoltaic pre-site selection, try to use the southern slope (sunny slope) and more flat areas to avoid areas with more northern slopes and steep slopes. Then estimate the area available for use. Mountainous photovoltaic 1MW land area is temporarily taken into consideration for 40-50 acres. It is possible to roughly estimate how much capacity the topographic map in the hand can be arranged.
24V LED Wall Washer
LED wall washer is also called LED Linear Light .Its shell adopts aluminum alloy lamp body and integral moulding processing technology to ensure good heat dissipation effect and effectively reduce the light decay during the use of LED. Using optical grade PMMA high-efficiency lens, low light loss, good illuminance. The unique switching constant current source technology ensures the stable operation of each LED.
Our other products range:LED Underground Light, LED Underwater Light, LED Wall Washer Light, LED Linear Light, LED Outdoor Flood Light, LED Garden Light , LED landscape light , LED Strip Light , LED Step Light etc.

LED Outdoor linear light bar,LED wall washer.LED outdoor wall washer.IP68 wall washer,Building wall washer,garden wall washer
SHENGYA LIGHTING TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. , https://www.syalighting.com
